Net profitable value refers to a capital budgeting analysis technique used to understand whether a long-term project will be profitable or not. Net Present Value (NPV) is defined as the present value of cash inflows and the present value of cash outflows over a certain period of time. The concept is widely used in investment planning and capital budgeting to analyse a project’s profitability. This is the result of calculations used to find the current value of a future stream of payments.
In the case of positive NPV, the outcome indicates the projected earnings from an investment or project exceed the anticipated costs in present dollars. It is assumed that an investment with a positive Net Present Value will be profitable, while a negative ratio will result in a net loss.
Now that the concept of NPV is clear to you, let’s discuss the advantages and disadvantages which are worth considering when working on the financial situation of a project or new investment.
The Advantages of Net Present Value
1. Considers the cost of capital and risk factors
2. Allows risk factors to enter into the calculation
3. Considers all cash flows from a project
4. Provides ranking information on projects while rationing
5. It lets you know if investments can create values
6. Does not work on the assumption of reinvestment
7. This is straightforward to calculate
8. They are additive in nature. So, in case you have excess capital or multiple projects, you are allowed to add projects for get a sense of aggregate wealth creation from all investable projects.
9. NPV accounts for investment size.
10. It offers an unambiguous measure.
11 NPV can easily recognise the time value of money.
12. NPV used cash flows instead of net earnings.
The Disadvantages of Net Present Value
1. Focuses on short-term projects due to future uncertainties
2. The only way of getting the value is through guesswork
3. While calculating the NPV, some of the costs are almost impossible to estimate
4. Fails to compare two projects of different sizes
5. With more time passing, the level of risks can get change for a project
6. It may not boost the return and earnings on equity for a company
7. NPV does not allow you to choose a specific discount rate
8. NPV is a difficult concept to grasp.
9. NPV tends to assume you can be accurate while assessing and predicting future cash flows.
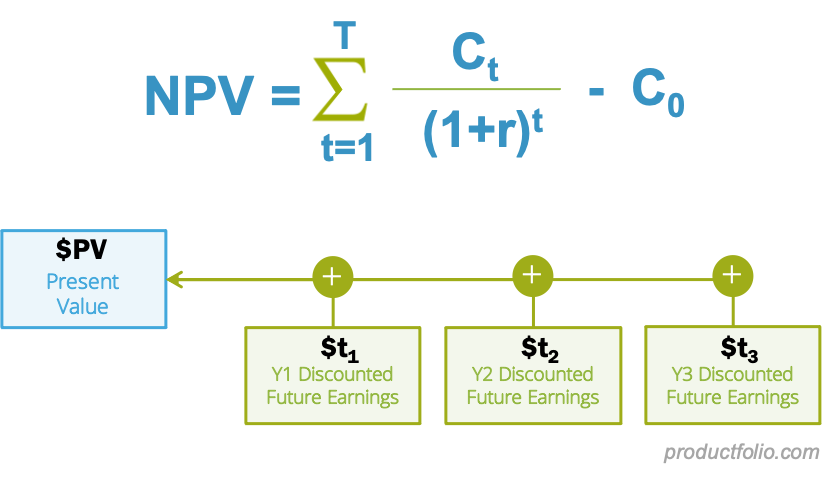
How to Calculate the NPV?
Here is how you can calculate the NPV or cash flow from a project that is going to be paid one year from now:
NPV = Cash flow/ (1+i) t
Where:
i = Required return or discount
t = Number of the time period
In case you are analysing a longer-term project with multiple cash flows, the formula for it will be as follows:
NPV =t / (1+i)t
Where:
Rt = net cash inflow- outflows during a single period t
i= discount rate or return that could be invested in alternative investment
t = Number of time periods
If you are someone who is not familiar with summation notation, you can refer to this easier way of remembering the concept of NPV:
NPV = Today’s value of the expected cash flows – Today’s value of invested cash
4 Vital Components in Calculating NPV
The formula of NPV formula comes with several parts. Its formula might vary for different types of cash flow streams. Below, I am going to dissect the formula into 4 components that are vital when you are calculating the NPV.
1. Future Cash flow
By taking the help of returns and inflation into account, future cash flow teams can differentiate between today’s present value of money and the future’s present value. Various situations may prompt you to calculate the future value of a series of cash flows. This may occur once or multiple times in the future for different amounts or a consistent cashflow.
2. Time period
The time period is an essential component of investment. It might take a one-time upfront investment. If the company expects a one-time cash flow in the future, it should identify the time period when they expect the return.
3. Interest rate
The NPV formula in the interest rate is also referred to as the discount rate. Companies tend to set this rate internally and often use the cost of capital when setting it.
4. Initial investment
During the analysis of NPV, it is quite common for a series of cash flows to start with an initial investment. Such cashflow is presented as a negative cash outflow, which is used for comparing the positive cash flow in the future. It is even common to assume such investment to happen in period 0.
SUMMING UP,
Although the concepts are not rocket science, these will be useful when crafting your net value assignments. Refer to this guideline to ace your net present value assignment.
AUTHOR BIO: Richard Watson has completed PhD in project management from one of the most prestigious universities in the UK. He is also associated with My Assignment help.com, where she offers net value assignment help solutions to finance or project management students.