The Speed Of Mild Is The Rate Restrict Of The Universe. Or Is It?
The velocity of mild traveling through a vacuum is precisely 299,792,458 meters (983,571,056 ft) per 2d. That’s about 186,282 miles in step with second—a popular constant regarded inside the equations as “c,” or the velocity of light.
According to physicist Albert Einstein’s principle of special relativity, on which a good deal of present-day physics is based, nothing within the universe can journey faster than light. The precept states that as count procedures the rate of mild, the mass of matter will become infinite. This way that the velocity of light acts as the rate limit on the entire universe. The velocity of mild is so irreversible that, It is used to outline worldwide popular measurements which include meters (and by way of extension, miles, toes, and inches), in step with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (opens in new tab). ) Through a few clever equations, it additionally helps to outline the kilogram and the temperature unit Kelvin.
Click here countspeed.com
But notwithstanding the velocity of mild’s popularity as a widespread regular, scientists and technology fiction writers alike spend time taking into account quicker-than-light journey. So some distance nobody has been capable of demonstrating the real warping, however that hasn’t slowed our collective problem in the direction of new stories, new inventions, and new regions of physics.
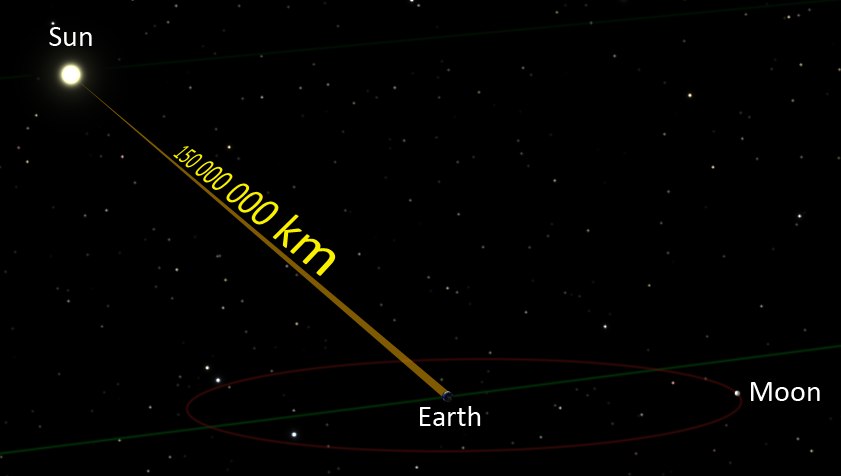
A mild year is a gap that mild can tour in a yr – about 6 trillion miles (10 trillion kilometers). This is one manner astronomers and physicists measure extreme distances in our universe.
Light travels from the Moon to our eyes in about 1 2nd, this means that the Moon is ready 1 light-second away. Sunlight takes about 8 minutes to reach our eyes, so the Sun is set eight light minutes away. Light from Alpha Centauri, the closest celebrity system to our personal, requires about 4.3 years to reach right here, so Alpha Centauri is four. Three light-years away.
“To get an idea of the size of a light-yr, take the circumference of the Earth (24,900 miles), lay it out in an immediate line, multiply the duration of the line through 7.5 (the corresponding distance is one mild-second), then 31.6 million. Keep even strains give up to quit,” NASA’s Glenn Research Center says on its internet site (opens in new tab). “The resulting distance is set 6 trillion (6,000,000,000,000) miles!”
You can get some more knowledge speed of light in water
Stars and different items past our sun gadget are placed everywhere from some light-years to a few billion mild-years away. And what astronomers “see” in the remote universe is actually history. When astronomers examine remote gadgets, they may be searching for mild that suggest the items they had been gifted while the light left them.
This idea lets astronomers look at the universe as it did after the Big Bang, which came about 13.8 billion years ago. Objects 10 billion light-years faraway from us seem to astronomers as if they appeared 10 billion years in the past – exceedingly soon after the beginning of the universe – not how they seem nowadays.
In the early fifth century, Greek philosophers including Empedocles and Aristotle disagreed on the character of the velocity of mild. Empedocles proposed that light, whatever it is made of, should journey and, consequently, need to have a fee for the journey. Aristotle wrote a refutation of Empedocles’ method in his own treatise, On the Sense and the Sensible (opens in new tab), arguing that not like sound and odor, mild must be immediate. Aristotle was direction incorrect, but it might take hundreds of years for anyone to show it.
In the mid-1600s, Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei spotted men standing on hills less than a mile apart. Each individual had a shielded lantern. One opened his lantern; When the alternative individual saw the flash, he opened it too. But Galileo’s experimental distance become no longer long sufficient for his individuals to report the velocity of mild. He could simplest conclude that light travels at least 10 instances quicker than sound.
In the 1670s, Danish astronomer Ole Römer tried to create a dependable timetable for sailors at sea, and according to NASA (opens in new tab), accidentally came up with a brand new quality estimate for the rate of light. To create an astronomical clock, he recorded the ideal timing of eclipses from Earth to Jupiter’s moon, Io. Over time, Romer observed that Io’s eclipses frequently differed from his calculations. They located that eclipses have been most behind schedule while Jupiter and Earth had been transferring away from each different, were seen whilst the planets have been drawing near, and were visible earlier whilst the planets had been at their nearest or farthest points. . This statement proven what we recognize these days as the Doppler effect, an alternate within the frequency of mild or sound emitted via a moving object that looks within the celestial global as a so-referred to as redshift, a shift in the direction of “redder”, in gadgets. Long wavelength far away from us. In a leap of intuition, Romer decided that mild was taking a measurable time to journey from Io to Earth.
Romer used his own approach to estimate the speed. She used the comments of Prakash. Since the size of the Solar System and the Earth’s orbit have been no longer yet exactly regarded, a 1998 paper within the American Journal of Physics (opens in new tab) argued, he changed into a chunk off. But in the long run, the scientists had a number to paint with. Romer’s calculations placed the rate of light at about 124,000 miles according to 2d (200,000 km/s).
In 1728, the English physicist James Bradley based totally a new set of calculations on the exchange in the apparent function of the stars due to the Earth’s adventure around the Sun. According to the American Physical Society (opens in new tab), he estimated the rate of mild to be 185,000 miles in line with the second (301,000 km/s) – correct to inside about 1% of the proper cost.
Two new tries within the mid-1800s delivered the problem back off to earth. French physicist Hippolyte Fizzou established a beam of light on a swiftly rotating toothed wheel, with a mirror set five miles (8 km) away to mirror it back to its supply. Varying the speed of the wheel allowed Feizhou to calculate how long it took for the light to travel via the hollow, to the adjacent replicate, and lower back through the gap. Another French physicist, Léon Foucault, used a rotating reflect rather than a wheel to carry out basically the equal test. The independent modes came within about 1,000 miles per 2d (1,609 km/s) of the velocity of light.