Biomass is a limitless regular material that comes from plants and organic entities. Biomass was the biggest wellspring of outright yearly US energy use until the mid-1800s. Biomass is a significant fuel in numerous nations, particularly for cooking and warming in non-industrialized nations. The utilization of biomass energy for the transportation and power period is expanding in many developed nations to avoid carbon dioxide discharges from the utilization of oil-based goods. In 2020, biomass conveyed roughly 5 quadrillions of British Warm Units (BTU) and around 5% of outright required energy use in the United States.
Biomass includes getting compound energy far from the sun. Plants produce biomass by photosynthesis. Biomass can be singed straightforwardly for heat or can be changed over into unlimited fluid and unpredictable energy through a grouping of cycles.
By visiting here you can get to know more about various topics.
Biomass focal points for energy include:
Wood and wood-dealing with squander – dull liquor from consuming, wood pellets, and wood chips, sawdust and waste from wood, and furniture production line, and squash and paper plants
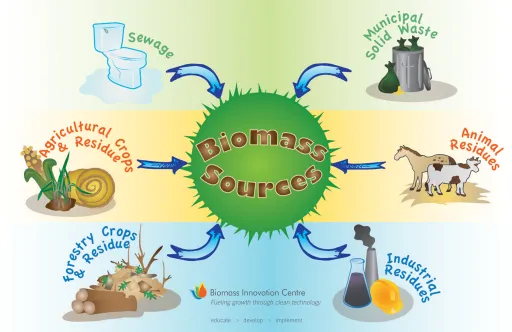
Agricultural produce and waste material – corn, soybeans, sugarcane, switchgrass, woody plants, and green development, and harvest and food dealing with development
Metropolitan braced squander incorporates biogenic materials – paper, cotton, and fleece things, and wastage of food, yard, and wood.
dung and human excrement.
changing biomass over completely to energy
Biomass is changed over into energy through a variety of cycles, including:
direct start (utilization) to create heat
Thermochemical changes to areas of strength for the frame, and liquid powers
Substance change for liquid filler improvement
By visiting here you can get to know more about how to find the slope of a line
Normal Change To Frame Fluid And Unstable Powers
Direct start is the most generally perceived methodology for changing over biomass into assistant energy. All that biomass can be scorched straightforwardly into warmed designs and water, to warm the cutting edge cycle, and to create power in steam turbines.
The thermochemical change of biomass includes pyrolysis and gasification. Both are hot deterioration processes in which the biomass feedstock material is warmed in shut, packed vessels, called gasifiers. They are basically an adjustment of cycle temperature and as opposed to how much oxygen is available during the cycle.
Pyrolysis warms regular materials to 800-900oF (400-500oC) in a basically complete decrease of free oxygen. Biomass pyrolysis produces power like charcoal, bio-oil, boundless diesel, methane, and hydrogen.
Hydrotreating is utilized to process bio-oil (conveyed by quick pyrolysis) with hydrogen under high temperature and strain as an impetus to make unlimited diesel, practical gas, and manageable stream fuel.
Gasification requires warming the regular material to 1,400-1700 °F (800-900 °C), with a controlled appearance of steam alongside free oxygen to shape a gas containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen, known as Also called blend gas or syngas. Volume is placed. Syngas can be utilized as fuel for diesel engines, gas turbines for warming, and for power age. Correspondingly hydrogen isolated from the gas can be honored to be gotten, and the hydrogen can be scorched or utilized in energy units. Syngas can be furthermore controlled to make fluid fuel utilizing the Fischer-Tropsch process.
How Much Biomass Is Utilized For Energy?
In 2020, biomass represented around 4,532 trillion British Warm Units (TBtu), or around 4.5 quadrillions Btu, and the outright U.S. around 4.9% of the expected energy use. Of that sum, around 2,101 TBtu were from wood and wood-fixed biomass, 2,000 TBtu were from biofuels (generally ethanol), and 430 TBtu were from the city squander biomass.
The biggest volume and outright yearly U.S. energy content as an energy material in the advanced and transportation areas. Energy material. Addresses the biggest degree of biomass use. Carpentry and paper undertakings use biomass to manage heat in consolidated power and power plants and to deliver power for their own utilization. Fluid biofuels (ethanol and biomass-based diesel) address the heft of the biomass utilization of the vehicle area.
The private and business areas use fuel and wood pellets for warming. The business area in like manner consumes, and once in a while sells, practical combustible gas disseminated in metropolitan sewage treatment workplaces and waste landfills.